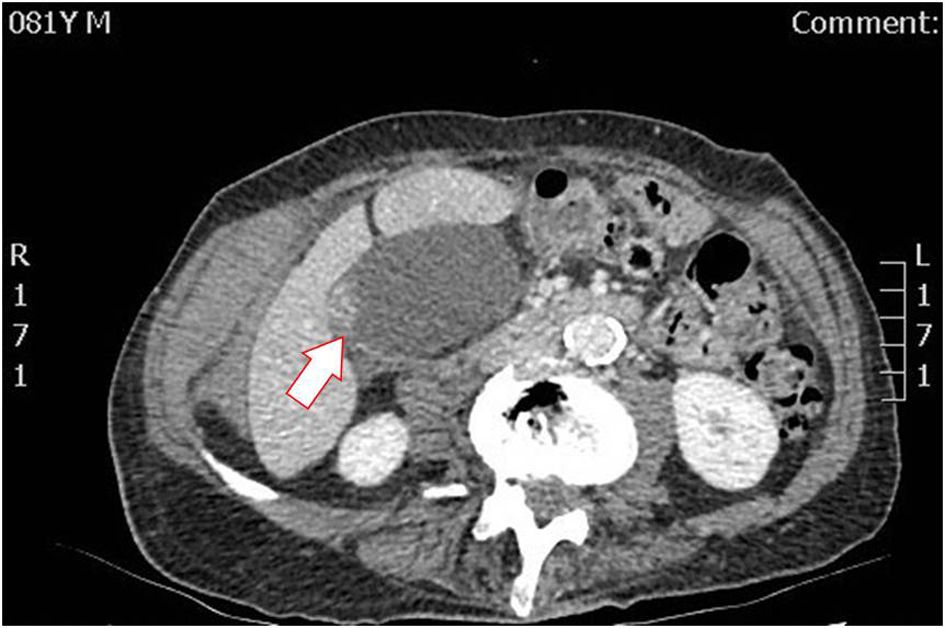
Figure 1. CT scan on admission day demonstrating enlargement of the gallbladder and focal thickening of the gallbladder wall. CT: computed tomography.
| Journal of Current Surgery, ISSN 1927-1298 print, 1927-1301 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Curr Surg and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.currentsurgery.org |
Case Report
Volume 10, Number 3, September 2020, pages 28-31
Gallbladder Torsion: A Rare Diagnostic Challenge
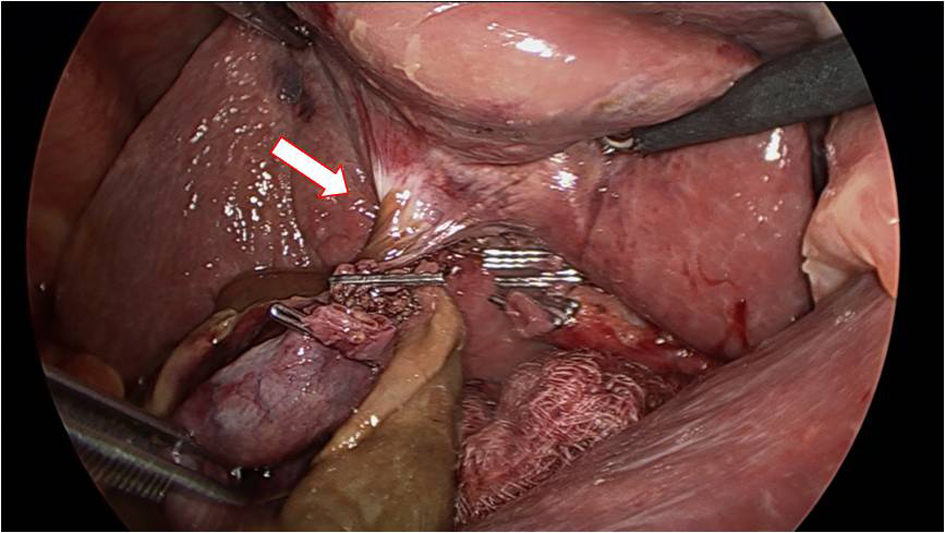
Figures

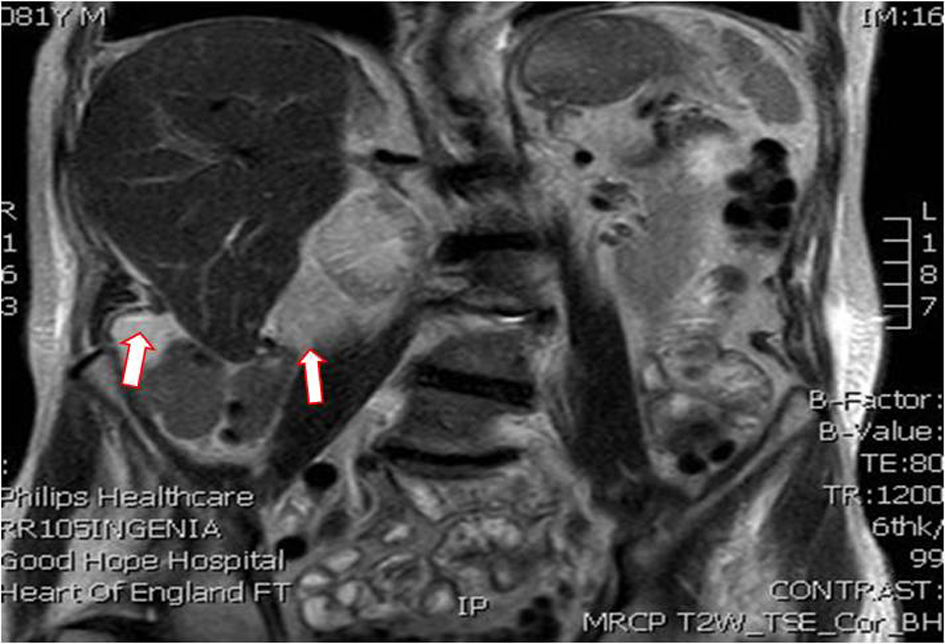
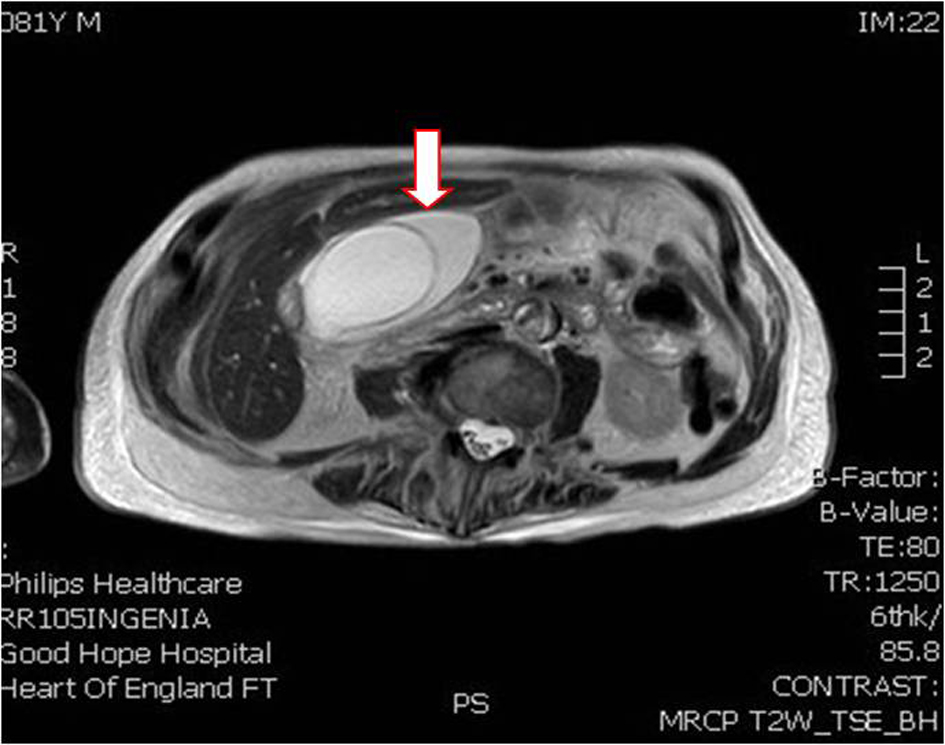
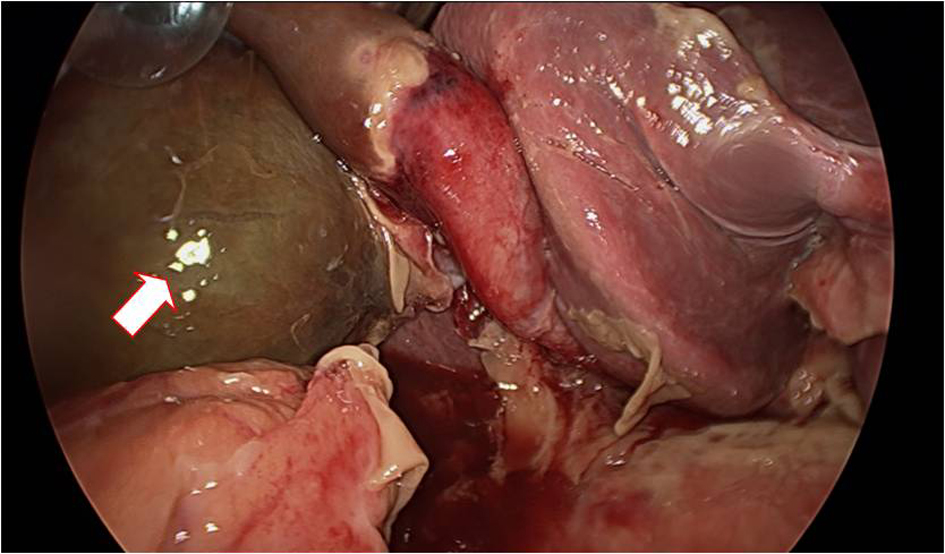
Table
| Parameter | Initial admission | Re-attendance date | Second day of hospitalization | Operation date | Second post-operative day | Institutional normal range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White cell count | 9.7 | 20.83 | 14.66 | 13.55 | 10.83 | (4.0 - 11.0) × 109 |
| Neutrophil count | 7.41 | 17.77 | 12.74 | 11.14 | 8.72 | (1.5 - 4.0) × 109 |
| Hemoglobin | 115 | 129 | 107 | 110 | 96 | 135 - 180 g/L |
| C-reactive protein | 47 | - | - | 154 | 130 | 0 - 5 mg/L |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 59 | 206 | 122 | 106 | 111 | 30 - 130 IU/L |
| Alanine transaminase | 16 | 190 | 98 | 67 | 82 | 0 - 55 IU/L |
| Bilirubin | 28 | 37 | 24 | 22 | 17 | < 21 µmol/L |
| Amylase | 57 | 29 | - | 24 | 21 | 15 - 25 IU/L |
| Plasma lactate | - | 1.4 | - | - | - | 0.5 - 2.2 mmol/L |